Goal and Objectives
It is important to explore all the different types of geoprocessing tools in ArcGIS in order to build models to solve real life issues. During this semester, we have been looking at sand mines in western Wisconsin more from the business side and how the companies can become more efficient. It is also important to build models for how the surroundings of the sand mines are impacted from a suitability, environmental, and cultural standpoint in Trempealeau County. This lab looks to answer those questions through the following objectives:
- Generate spatial data layer to meet geologic criteria
- Generate spatial data layer to meet land use land cover criteria
- Generate a spatial data layer to meet distance to railroads criteria
- Generate a spatial data layer to meet the slope criteria
- Generate a spatial data layer to meet the water-table depth criteria
Methods
Find
suitable land for the geologic criteria
The two geologic units that are mined for frac sand are from the Jordan Formation and the Wonowac Formation. For the first map, those desired areas of geologic formations are made into one color while the rest of the geologic units are made in another color. This helps show where the mine able areas are.
Find suitable land for the land use criteria
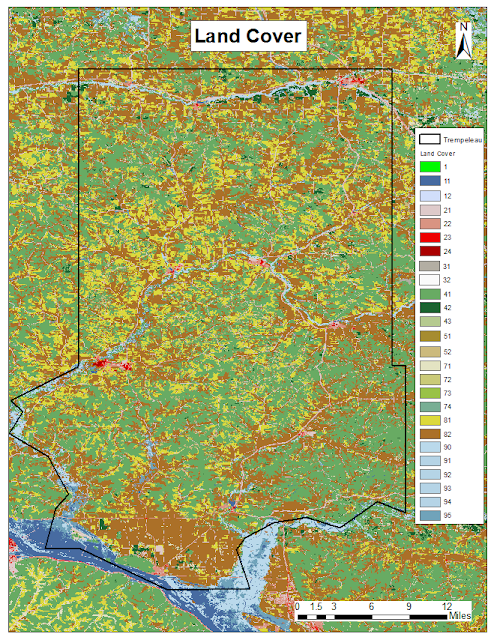
By comparing the National Land Cover Data and the map the was created in the previous step, I noticed that the land cover in the areas common for frac sand mining is deciduous forest. This type of land is dominated by trees that are generally greater than 5 meters tall, and greater than 20% of total vegetation cover. More than 75% of the tree species shed foliage simultaneously in response to seasonal change.
Find suitable land for the proximity to railroads criteria
To see the distance away from each railroad terminal in every direction, the Euclidean distance tool can be used. The result shows a nice radial map that gives a quick visual representation of distances to each railroad terminal.
Find suitable land for the slope criteria
It is important to find the slope in an area especially for a business like a sand mine. The 3-D analyst tool "Slope" was used to find this factor. A percent rise was used for the output measurement.
Find water table depth
The attribute that shows water depth in the coverage file is "wt_elev" which is the water table elevation. The tool used to show the water table depth properly is the "Topo to Raster" tool. The coverage file for the water table is originally imported into ArcGIS as a vector feature class. This tool allows us to see continuous data for water table depth, which is probably more realistic than just a polyline.
The two geologic units that are mined for frac sand are from the Jordan Formation and the Wonowac Formation. For the first map, those desired areas of geologic formations are made into one color while the rest of the geologic units are made in another color. This helps show where the mine able areas are.
Find suitable land for the land use criteria
By comparing the National Land Cover Data and the map the was created in the previous step, I noticed that the land cover in the areas common for frac sand mining is deciduous forest. This type of land is dominated by trees that are generally greater than 5 meters tall, and greater than 20% of total vegetation cover. More than 75% of the tree species shed foliage simultaneously in response to seasonal change.
Find suitable land for the proximity to railroads criteria
To see the distance away from each railroad terminal in every direction, the Euclidean distance tool can be used. The result shows a nice radial map that gives a quick visual representation of distances to each railroad terminal.
Find suitable land for the slope criteria
It is important to find the slope in an area especially for a business like a sand mine. The 3-D analyst tool "Slope" was used to find this factor. A percent rise was used for the output measurement.
Find water table depth
The attribute that shows water depth in the coverage file is "wt_elev" which is the water table elevation. The tool used to show the water table depth properly is the "Topo to Raster" tool. The coverage file for the water table is originally imported into ArcGIS as a vector feature class. This tool allows us to see continuous data for water table depth, which is probably more realistic than just a polyline.
Results
Find suitable land for the geologic criteria
Find suitable land for the land use criteria
 |
| Based on National Land Cover Data, the yellow areas show land that possibly has go land cover for frac sand. I have reclassed all other types of land cover in red. |
Find suitable land for the proximity to railroads criteria
 |
| Red dots represent the railroad terminals and the colors represent the distance from each railroad termainal. |
 |
| Slope that was calculated from elevation data. The lighter colors represent lower elevations. The numbers rank the elevation values; the higher the elevation, the higher the rank. |
Find water table depth
 |
| This is a map of Trempealeau County that shows the depth of the water table. |
http://wisconsingeologicalsurvey.org/gis.htm